The service sector is a vast field encompassing various activities, including wholesale and retail trade, restaurants and hotels, transportation, storage, information and communications, financial services, insurance, real estate, business services, social and personal services, and government services. Below are the key indicators of this sector in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and other GCC countries:
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia:
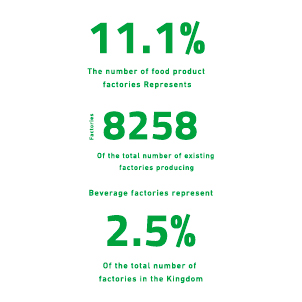
- Number of operating factories: 8,258 factories.
- Licensed workforce: 968,121 workers.
- Total capital of these factories: SAR 1,256,616 million.
- The largest industrial activity in terms of the number of factories is non-metallic minerals (1,641 factories), followed by rubber and plastics (1,122 factories).
- Riyadh holds the highest percentage of factories (3,332 factories), followed by the Eastern Region (1,877 factories) and Makkah Region (1,741 factories).
- Small factories represent 43.7% of total factories (3,671 factories) with 111,354 workers.
- Medium factories represent 46.6% of total factories (3,907 factories) with 379,342 workers.
- Large factories represent 9.7% of total factories (813 factories) with 477,425 workers.
- There are 1,801 factories under construction in Saudi Arabia, employing an estimated 78,650 licensed workers. The total capital of these factories is SAR 68,481 million.
- Riyadh accounts for 40.4% of factories under construction (728 factories).
United Arab Emirates:
- Total number of factories: 6,481 factories.
- Workforce: 737,126 workers.
- Number of establishments in the manufacturing sector: 32,654 establishments.
- The production value of the manufacturing sector: AED 448,127 million.
- The largest industrial activity by production value is the manufacture of coke and refined petroleum products, producing AED 119,787 million, according to the latest official statistics.
- Industrial exports exceed AED 240 billion.
- The UAE aspires to rank 25th in the Global Competitiveness Index for industrial performance, improving from its previous rank of 38.
- The state supports the establishment of 13,500 small and medium enterprises.
Sultanate of Oman:
- Number of manufacturing institutions: 61,217.
- Workforce in the manufacturing sector: 237,000 workers.
- The manufacturing sector contributes 9.6% to Oman’s GDP.
- The contribution of manufacturing exports to total exports is 31.4%.
- The manufacturing sector has achieved a growth rate of 6% over the past five years.
Kuwait:
- Number of industrial establishments: 5,539 establishments.
- Workforce in the sector: 160,654 workers.
- Total production value: KWD 35,929,708,000.
- Establishments with 1-10 employees: 4,526 establishments, employing 24,048 workers with a production value of KWD 250,322,000.
- Establishments with 11-19 employees: 464 establishments, employing 6,871 workers with a production value of KWD 113,126,000.
- Establishments with more than 20 employees: 549 establishments, employing 129,735 workers with a production value of KWD 35,566,260,000.
Qatar:
- Number of industrial establishments: 3,467 establishments.
- Workforce: 161,872 workers.
- Small and medium industries account for approximately 84% of the total factories in the country.
- The manufacturing sector contributes 9.2% to Qatar’s GDP.
- Establishments with fewer than 10 employees: 1,799 establishments, employing 8,305 workers.
- Establishments with more than 10 employees: 1,668 establishments, employing 153,567 workers.